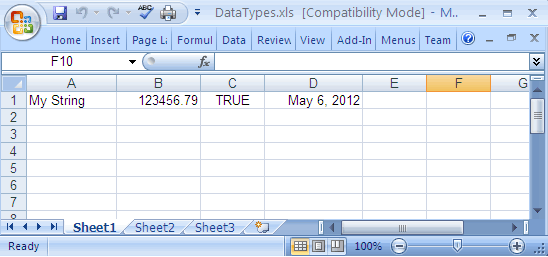
How to read different Cell Data types
Java Excel API is an open source java library to read, write and modify Excel spread sheets.
This requires the library jxl-2.6.12.jar to be in classpath.
The following example shows how to read the contents of different Cell Data types.
package com.bethecoder.tutorials.jexcelapi.read; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Date; import jxl.BooleanFormulaCell; import jxl.Cell; import jxl.CellType; import jxl.DateCell; import jxl.LabelCell; import jxl.NumberCell; import jxl.Sheet; import jxl.Workbook; import jxl.read.biff.BiffException; public class GetDataTypesTest { /** * @param args * @throws IOException * @throws BiffException */ public static void main ( String [] args ) throws BiffException, IOException { Workbook workbook = Workbook.getWorkbook ( new File ( "C:/JXL/DataTypes.xls" )) ; Sheet firstSheet = workbook.getSheet ( 0 ) ; Cell a1 = firstSheet.getCell ( 0 , 0 ) ; //String cell Cell a2 = firstSheet.getCell ( 1 , 0 ) ; //Number cell Cell a3 = firstSheet.getCell ( 2 , 0 ) ; //Boolean function cell Cell a4 = firstSheet.getCell ( 3 , 0 ) ; //Date cell printCell ( a1 ) ; printCell ( a2 ) ; printCell ( a3 ) ; printCell ( a4 ) ; //Close and free allocated memory workbook.close () ; } private static void printCell ( Cell cell ) { System.out.print ( "Cell[" + cell.getRow () + "-row, " + cell.getColumn () + "-col] : " ) ; if ( cell.getType () == CellType.LABEL ) { LabelCell labelCell = ( LabelCell ) cell; String str = labelCell.getString () ; System.out.println ( str ) ; } else if ( cell.getType () == CellType.NUMBER ) { NumberCell numCell = ( NumberCell ) cell; double num = numCell.getValue () ; System.out.println ( num ) ; } else if ( cell.getType () == CellType.DATE ) { DateCell dateCell = ( DateCell ) cell; Date date = dateCell.getDate () ; System.out.println ( date ) ; } else if ( cell.getType () == CellType.BOOLEAN_FORMULA ) { BooleanFormulaCell boolFormulaCell = ( BooleanFormulaCell ) cell; boolean value = boolFormulaCell.getValue () ; System.out.println ( value ) ; } } }
Cell[0-row, 0-col] : My String
Cell[0-row, 1-col] : 123456.789
Cell[0-row, 2-col] : true
Cell[0-row, 3-col] : Sun May 06 05:30:00 IST 2012